The Node Concept
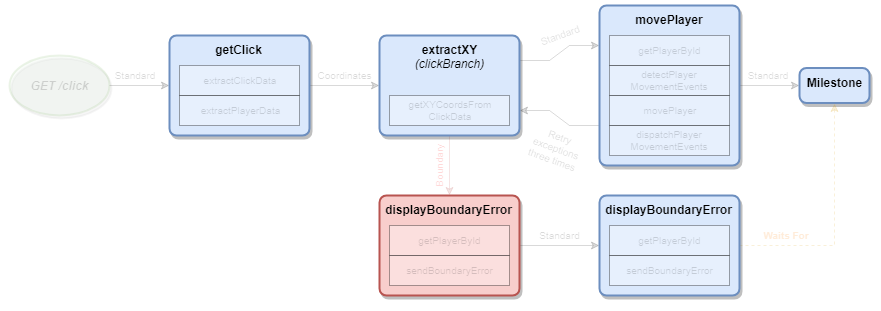
Nodes contain Actions and connect to one or more Channels. They receive events from Channels and pass events to Channels.
Actions
Actions are individual axioms about your business rules represented by JavaScript. Within an action, you can do the following:
dispatch(eventName): Places an Event, by name, on the Event Queue.set(key, value): Commits the value to the Request state based on the key.get(key): Retrieves the current Request state based on the key.toStore(name, key, value): Sets the value to the named store based on the key.fromStore(name, key): Retrieves the keyed value from the name store.schedule(action, strategy): Schedules an Action to be processed at the next Milestone.waitFor(stepId, callback): Tells the Node to dispatch Channel events only when the step specified by thestepIdhas finished.
If a Node or Milestone has multiple Actions, they will be executed in sequence. Each time an Action is ran, lifecycle information about that information is emitted.
When defining an Action, you have to pass in a function that performs the actual action. This function cannot be an arrow function due to limitations in how .call() works. You have to use standard Functions or Promises with Actions.
Milestones
Milestones will execute all scheduled Actions that have been accumulated. Scheduled actions will be executed in the order they have been scheduled. Once those Actions are completed, the Request will have no more Scheduled actions pending. It is HIGHLY recommended to schedule Actions that are related to retrieving or committing information to persistent, remote, and/or non-idempotent services. If you don’t do this, you will experience difficult-to-reverse transactional situations during parallel processing or random order of exeuction during sequential processing. Like Nodes, Milestones also connect to one or more Channels.
FlowNote
This example defines Nodes and the Actions they will execute.
node someNode = action1
node anotherNode = action2, action3
node lastNode = action4, action5, action6
Node, Milestone, and Action names can only be letters, numbers, or periods.
This defines a Flow as a single Node.
flow example(GET /example) = someNode
This defines a Flow as a single Node which leads to a Milestone (*) that executes any accumulated Scheduled Actions.
flow example(GET /example) = someNode*
Examples
- This action doubles the value of x.
- This action will wait 1000 milliseconds before multiplying y by 10.
- This action will set y equal to x minus from y.
- Here’s an array of Actions, ready to be
importedby a FlowNote file.
Documentation
( Installation | Features | Use Cases | Language | Application | Flow | Nodes | Channels | Contribution Overview | Roadmap | Known Problems )